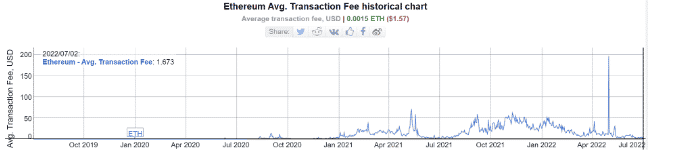
Ethereum’s average gas fees drop below $1.57 which is the lowest level since 2020 as we can see more in today’s Ethereum news.
For two years between 2021 and 2022, the average gas fee required by the network was about $40 and in May this year, the highest average daily gas cost was recorded at $196. The Ethereum ecosystem’s biggest roadblock to mainstream dominance is attributed often to the high transaction fees or gas fees required to complete a transaction however with Ethereum’s average gas fees dropping, the narrative is about to change.
XCarnival was attacked on June 26, 2022 and suspended part of the protocol. XCarnival officials will give 0xb7CBB4d43F1e08327A90B32A8417688C9D0B800a owner 1500 ETH bounty.
At the same time, XCarnival officals explicitly exempt the person from legal action.By XCarnival team
— XCarnival (@XCarnival_Lab) June 27, 2022
The average transaction fee on the ETH blockchain dropped to $1.57 which is a number only seen in December 2020. However, starting in January 2021, the gas fees surged owing to the hype around NFTs and DEFI as a promising bull market. For two years, the average gas fee required by the Ethereum network was about $40 with May 1 of 2022 recording the highest gas cost of $196 as the data from BitInfoCharts show.
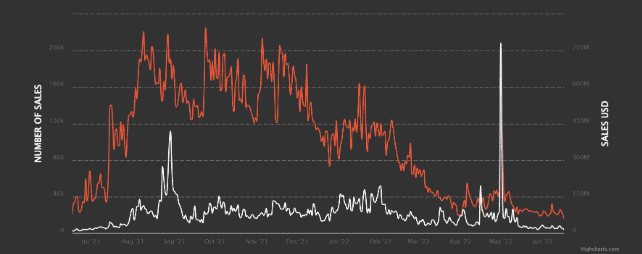
Supporting the sudden drop in gas prices, the reports show that the daily NFT sales also dropped to a one-year low and the NFT ecosystem recorded the worst performance of the year in June with the total number of daily sales dropping to 19,000 with an estimated value of $13.8 million. In November 2021, the investors reproted some outrageous gas fees and the ETH co-founder Vitalik Buterin published a decreased cost and cap proposal to reduce the levels of strain on the network. Buterin proposed a short-term solution to cut rollup costs by launching a call data limit per bock to low gas costs.
Ethereum liquditiy provider XCarnival recovered 1467 ETH a day after suffering an exploit that drained 3087 ETH that was worth $3.8 million. Blockchain investigator Peckshield explained:
“The hack is made possible by allowing a withdrawn pledged NFT to be still used as the collateral, which is then exploited by the hacker to drain assets from the pool.”
DC Forecasts is a leader in many crypto news categories, striving for the highest journalistic standards and abiding by a strict set of editorial policies. If you are interested to offer your expertise or contribute to our news website, feel free to contact us at [email protected]























Discussion about this post