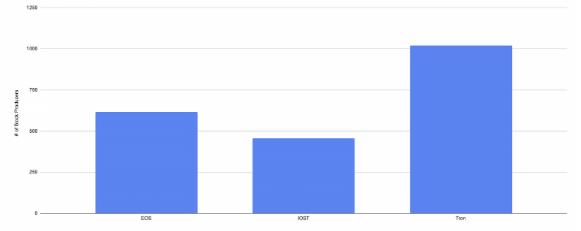
The EOS Ecosystem dies out slowly despite raising the $4.1 billion during its ICO. The blockchain was unable to unseat Ethereum and its shortcomings provide a strong case study on how money is not enough to buy crypto adoption so let’s find out more in the upcoming EOS news.
EOS conducted one of the biggest ICOs in the world and attracted more than half of what was invested in 2017 all for good reasons. The network has enticing technology that outdoes Ethereum at scalability and its ease of development. EOS-based dapps don’t really ask the users to pay for transactions which makes them more friendly than the ETH-based dapps.
If EOS solves the biggest problems of Ethereum, why isn’t it still in the lead? It turns out, some technological concepts and a lot of money are not the only features that attract developers and users. While EOS was able to garner a huge community at its launch, it failed to retain it. The platform’s centralization and prohibitive usage costs forced a lot to migrate to another blockchain. The project needs a strategic approach in order to prevent the EOS ecosystem from dying out.
The discussions between the block producers revealed that the network was supported by the grassroots movement which is a healthy element for any public blockchain. However, as the stakes increased, bigger players joined and took over EOS governance. Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum, EOS utilizes the Delegated Proof of Stake consensus which plays a huge role in the formation in the network’s current set up.
Only 21 nodes can produce the blocks and therefore are able to earn rewards. The incentive to join the coveted block production creates strong competition which theoretically is quite beneficial for the network overall. In practice, however, there are some complications. The election of BPs is based on how many votes will one candidate receives. The EOS constitution prohibits gaming the system to make profits and it is designed to prevent this kind of governance capture by the block producers which has no impact on the network.
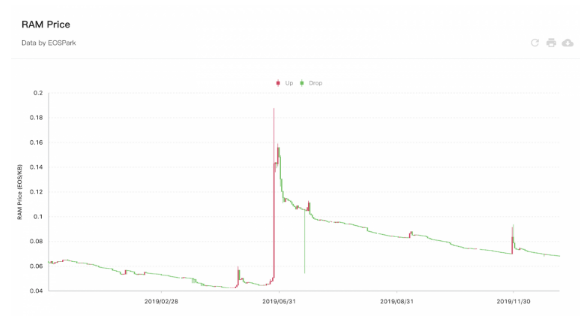
The EOS developers are now getting to the cost of onboarding new users and in line with the EOS architecture, deploying a dapp requires renting resources such as NET and CPU or buying a RAM. If the Dapp user base increases, more resources will be needed so the developers can allocate them. EOS resources create secondary markets as the RAM prices can increase which dampens the Dapp development. For example, Scaling Voice on EOS will require paying $2 billion for the accounts creation only.
DC Forecasts is a leader in many crypto news categories, striving for the highest journalistic standards and abiding by a strict set of editorial policies. If you are interested to offer your expertise or contribute to our news website, feel free to contact us at editor@dcforecasts.com






















Discussion about this post